Understanding Skull Base Anatomy: Structure, Functions, and Clinical Significance
Introduction
The skull base is one of the most complex and important areas of human anatomy. It forms the floor of the cranial cavity and separates the brain from other structures such as the nasal passages and the eyes. Understanding the anatomy of the skull base is essential for medical professionals, especially those involved in neurology, otolaryngology, and surgery. This blog will explore the structure, functions, and clinical significance of the skull base.
Structure of the Skull Base
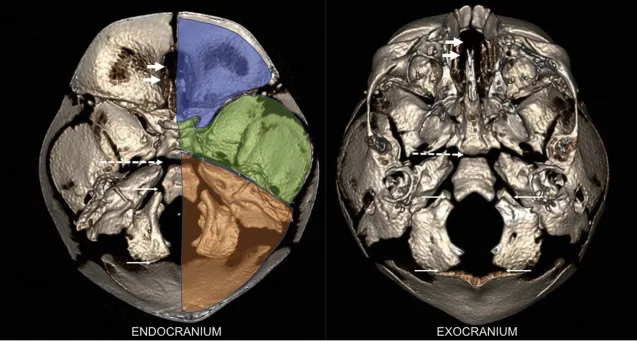
The skull base is divided into three distinct regions: the anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossae. Each of these regions houses different structures and has specific anatomical features.
- Anterior Cranial Fossa:
The anterior cranial fossa is located at the front of the skull and supports the frontal lobes of the brain. It includes the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone, which is a critical structure for the sense of smell, as it allows the olfactory nerves to pass through tiny openings to the nasal cavity. - Middle Cranial Fossa:
Situated behind the anterior fossa, the middle cranial fossa is deeper and houses the temporal lobes of the brain. It contains several important foramina (openings) through which nerves and blood vessels pass. The sella turcica, a depression in the sphenoid bone, is also located here and holds the pituitary gland, a key player in hormone regulation. - Posterior Cranial Fossa:
The posterior cranial fossa is the deepest and largest of the three fossae, located at the back of the skull. It accommodates the cerebellum, brainstem, and various cranial nerves. The foramen magnum, a large opening at the base of the skull, is a crucial structure in this region, allowing the spinal cord to connect to the brain.
Clinical Significance
The skull base anatomy is not only complex but also clinically significant, as it is involved in various medical conditions and surgical procedures.
- Tumors and Lesions:
Tumors, such as meningiomas and pituitary adenomas, can develop in the skull base region, requiring intricate surgical approaches due to the proximity of critical structures. - Skull Base Surgery:
Surgical procedures involving the skull base are among the most challenging in medicine. They require a deep understanding of the anatomy to avoid damaging essential nerves and blood vessels. Endoscopic techniques have revolutionized skull base surgery, allowing for less invasive approaches. - Trauma:
Fractures of the skull base can lead to serious complications, such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks, which increase the risk of infections like meningitis.
Functions of the Skull Base
The skull base serves several critical functions:
- Support and Protection:
The skull base supports the brain and protects vital structures such as nerves and blood vessels. It acts as a barrier between the brain and other areas like the nasal cavity and the eyes. - Passageways for Nerves and Blood Vessels:
The skull base has numerous openings, called foramina, that allow cranial nerves and blood vessels to pass through, facilitating communication between the brain and the rest of the body. - Attachment for Muscles:
Various muscles, particularly those involved in chewing and head movement, attach to the skull base, making it essential for proper function and movement.
Conclusion
The skull base is a vital area of human anatomy that plays a crucial role in supporting the brain, protecting important structures, and allowing the passage of nerves and blood vessels. Its complexity makes it a significant focus in various medical fields, particularly in the diagnosis and treatment of conditions affecting the brain and surrounding areas. Understanding the skull base’s anatomy is essential for anyone involved in the medical care of the head and brain. For those interested in learning more about skull base anatomy or related medical fields, consider consulting with specialists or enrolling in advanced anatomy courses that offer in-depth study and practical experience.
FAQs
1. What are the main regions of the skull base?
The skull base is divided into three regions: the anterior cranial fossa, the middle cranial fossa, and the posterior cranial fossa, each housing different structures of the brain.
2. Why is the skull base important in surgery?
The skull base is crucial in surgery due to its proximity to vital nerves and blood vessels. Specialized surgical techniques are required to treat conditions like tumors without damaging critical structures.
3. What are common conditions affecting the skull base?
Common conditions include tumors, such as meningiomas and pituitary adenomas, trauma leading to fractures, and complications like cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks.





